Is it Legal to Fly a Drone Over a Private Property? How Low Can You Fly?
Explore the complexities of flying drones over private property

Image Source: Builderhomesource
Drones have become a common sight in the skies in the US, embraced by both hobbyists and professionals for varying purposes. Everyone loves to soar through the sky and capture some of the most mesmerizing sights around them. However, there is a valid concern about flying drones over private property. Questions such as ‘How low can you fly a drone over private property?’ and ‘Is it legal to fly a drone over private property?’ need to be answered for the safe and respectable use of these devices. The objective of this article is to do just that.
So, without further waiting, let’s get onto it.
Is it Legal to Fly a Drone over Private Property?
First things first, we must discuss the legality of flying a drone over private property before anything else.

Image Source: Govtech
When it comes to drone flying, the sky is not quite the limit. The FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) oversees the national airspace, and while their regulations are designed to keep us safe, they also touch upon our rights on the ground. In simplest terms, when your drone descends over someone’s private property, privacy concerns come into play.
Federal Law in the US does not explicitly prohibit drones over private property, but state and local laws have different interpretations. There are local laws, often created to protect property owner’s rights, that drone users need to be mindful of. These laws include restrictions on surveillance, trespass, and nuisance and affect how close one can get to a private property without permission. It goes without saying that you need to be aware of these laws if you do not want to run afoul of them.
State-Specific Drone Laws Over Private Property
As stated, the federal authority, i.e., the FAA, does not have specific regulations on the minimum height that one can fly their drone – local laws cover these. Now, because of their local nature and different interpretations of privacy, these local laws differ from state to state. We would recommend connecting with the local authority to understand the guidelines in your area better.
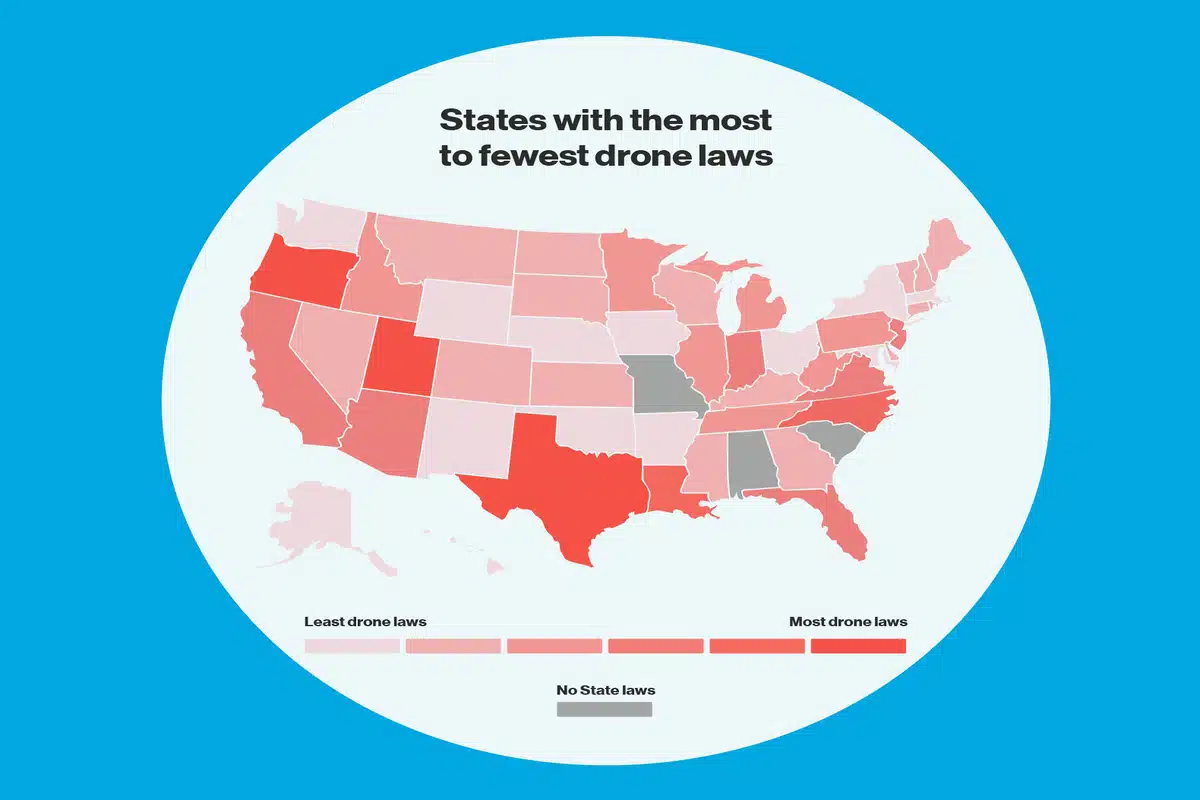
Image Source: Digital Information World
Here is an overview of a few states and their laws concerning the use of a drone over private property.
Alaska
There are no specific state laws that restrict drones from flying over private property. However, there are trespassing laws that one can be charged with if they hover a drone over someone’s property without permission. So, the general rule to follow is simply to avoid flying drones over private property,
New York
New York is one example of a state that has been proactive in addressing privacy concerns related to drone usage. The New York State Drone Law includes provisions that prohibit the use of drones for surveillance without consent and interference with first responders during emergencies. Doing so could have legal repercussions.
Illinois
Illinois is another state that has directly addressed the use of drones. The Illinois Drone Act prohibits the use of drones to interfere with hunters or fishers, to harass individuals, or to interfere with first responders. Note that the law does not directly explicitly ban drones from playing over private property, but there is a reasonable expectation of privacy embedded in it.
California
The Golden State has stringent privacy laws in its state constitution, and it includes the use of drones as well. California Civil Code Section 1708.8 prohibits the use of drones to capture images or video of someone in a way that invades their privacy. In simplest terms, there is a ‘no-fly zone’ for drones over private homes without explicit permission.
Texas
Texas is another state that champions privacy, especially when it comes to property. The Texas Privacy Act prohibits the use of unmanned aircraft to capture images without the consent of the individual or property owner.
Florida
The final state that we will cover is Florida. We do so because Florida laws reflect a balance between privacy and the burgeoning drone industry.
Florida’s Freedom from Unwarranted Surveillance Act prohibits individuals from using a drone to surveil private property – without permission from the owner. However, there are exceptions crafted for certain commercial operations, provided they comply with the FAA’s regulations.
Through these six state examples, we have tried to cover the different types of local laws that are in place regarding flying drones over private property.
Enforcement and Penalties
Flying a drone over private property without permission or in a manner that violates their privacy can lead to significant legal consequences.
- Drone operators may be subject to monetary penalties
- Property owners can initiate civil lawsuits for trespassing or invasion of privacy
- In some jurisdictions, severe violations could lead to criminal charges
- Detention or Arrest of the drone user
- The FAA may levy its own sanctions, including fines or revocation of a drone operator’s license.

Image Source: Rnz
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
As a private citizen, you cannot unilaterally declare your property a no-fly zone. However, you can petition the FAA to recognize the airspace for restriction, though it is unlikely to bore fruitful results. These petitions are typically approved for entities like airports or government facilities.
Yes, you can fly your drone around your neighbourhood without any issues. However, you must follow FAA regulations, respect local laws concerning privacy and nuisance, and ensure that you do not fly over private property without consent.
The FAA mandates that drones should not fly higher than 400 feet above ground level in uncontrolled airspace; however, there is no specific federal regulation for minimum altitude over private property.
Conclusion
It is crucial for drone users to respect the rights of property owners while flying around their space – something we have tried to emphasize in this article. The legalities of flying a drone over someone else’s property may vary from location to location, but the gist of it is that you must respect the privacy of others. You must stay up-to-date with the FAA’s guidelines and local laws to fly your drone responsibly!
Why trust Brownspace?
At Brownspace, we write about what matters most to the audience. We do well-researched work to provide in-depth knowledge of drones. Additionally, we interview people using drones to ensure the credibility of the drones used and offer real-life user experience to our readers.

Hi, drone enthusiasts! Born with a natural curiosity for the skies, I developed a love for drones early in life. I began flying drones in 2017 and have since piloted some of the best drones available, such as the Yuneec Typhoon, DJI Mini, Mavic Pro, Hover Camera, and Phantom 3. With passion for drones and expertise gained over the years, I would love to share my knowledge of drones at Brownspace. Stay tuned for an insider’s perspective about drones.










